This module includes centrality-related algorithms.
| pagerank | Calculate the PageRank of each vertex. |
| betweenness | Calculate the betweenness centrality for each vertex and edge. |
| central_point_dominance | Calculate the central point dominance of the graph, given the betweenness centrality of each vertex. |
| closeness | Calculate the closeness centrality for each vertex. |
| eigenvector | Calculate the eigenvector centrality of each vertex in the graph, as well as the largest eigenvalue. |
| katz | Calculate the Katz centrality of each vertex in the graph. |
| hits | Calculate the authority and hub centralities of each vertex in the graph. |
| eigentrust | Calculate the eigentrust centrality of each vertex in the graph. |
| trust_transitivity | Calculate the pervasive trust transitivity between chosen (or all) vertices in the graph. |
Calculate the PageRank of each vertex.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
damping : float, optional (default: 0.85)
pers : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
weight : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
prop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
epsilon : float, optional (default: 1e-6)
max_iter : int, optional (default: None)
ret_iter : bool, optional (default: False)
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | pagerank : PropertyMap
|
See also
Notes
The value of PageRank [pagerank-wikipedia] of vertex v, \(PR(v)\), is given iteratively by the relation:
where \(\Gamma^{-}(v)\) are the in-neighbours of v, \(d^{+}(w)\) is the out-degree of w, and d is a damping factor.
If a personalization property \(p(v)\) is given, the definition becomes:
If edge weights are also given, the equation is then generalized to:
where \(d^{+}(u)=\sum_{y}A_{u,y}w_{u\to y}\) is redefined to be the sum of the weights of the out-going edges from u.
The implemented algorithm progressively iterates the above equations, until it no longer changes, according to the parameter epsilon. It has a topology-dependent running time.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
| [pagerank-wikipedia] | (1, 2) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pagerank |
| [lawrence-pagerank-1998] | P. Lawrence, B. Sergey, M. Rajeev, W. Terry, “The pagerank citation ranking: Bringing order to the web”, Technical report, Stanford University, 1998 |
| [Langville-survey-2005] | A. N. Langville, C. D. Meyer, “A Survey of Eigenvector Methods for Web Information Retrieval”, SIAM Review, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 135-161, 2005, DOI: 10.1137/S0036144503424786 |
| [adamic-polblogs] | L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> pr = gt.pagerank(g)
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=pr,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(pr, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=pr, output="polblogs_pr.pdf")
<...>
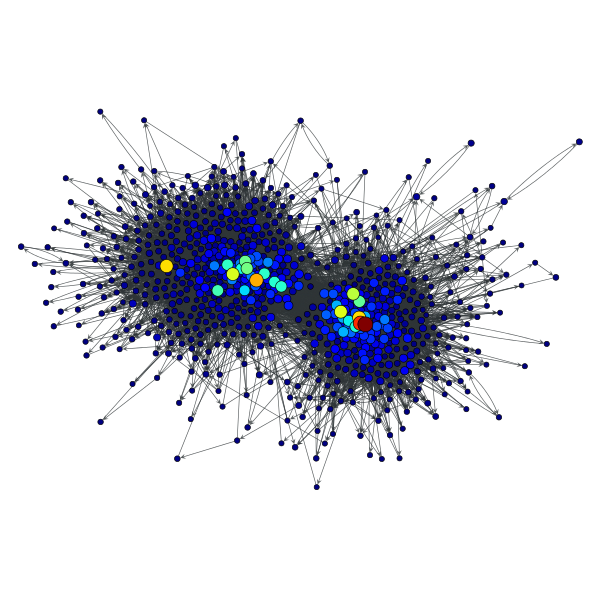
PageRank values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs].
Now with a personalization vector, and edge weights:
>>> d = g.degree_property_map("total")
>>> periphery = d.a <= 2
>>> p = g.new_vertex_property("double")
>>> p.a[periphery] = 100
>>> pr = gt.pagerank(g, pers=p)
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=pr,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(pr, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=pr, output="polblogs_pr_pers.pdf")
<...>
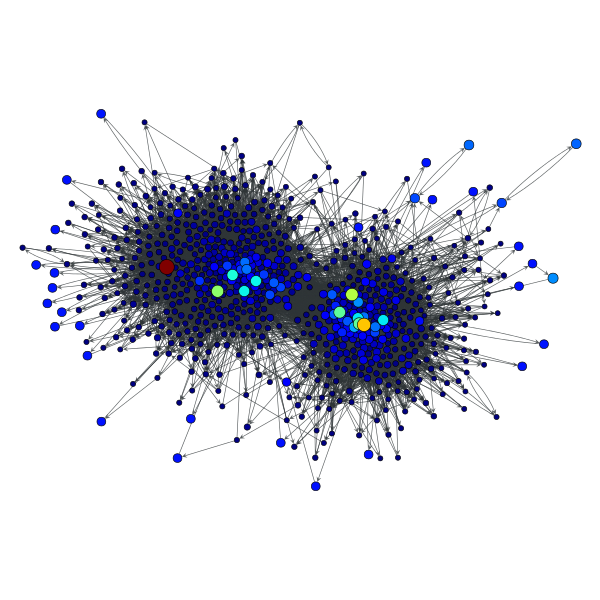
Personalized PageRank values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs], where vertices with very low degree are given artificially high scores.
Calculate the betweenness centrality for each vertex and edge.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
vprop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
eprop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
weight : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
norm : bool, optional (default: True)
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | vertex_betweenness : A vertex property map with the vertex betweenness values. edge_betweenness : An edge property map with the edge betweenness values. |
See also
Notes
Betweenness centrality of a vertex \(C_B(v)\) is defined as,
where \(\sigma_{st}\) is the number of shortest geodesic paths from s to t, and \(\sigma_{st}(v)\) is the number of shortest geodesic paths from s to t that pass through a vertex v. This may be normalised by dividing through the number of pairs of vertices not including v, which is \((n-1)(n-2)/2\).
The algorithm used here is defined in [brandes-faster-2001], and has a complexity of \(O(VE)\) for unweighted graphs and \(O(VE + V(V+E) \log V)\) for weighted graphs. The space complexity is \(O(VE)\).
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
| [betweenness-wikipedia] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centrality#Betweenness_centrality |
| [brandes-faster-2001] | (1, 2) U. Brandes, “A faster algorithm for betweenness centrality”, Journal of Mathematical Sociology, 2001, DOI: 10.1080/0022250X.2001.9990249 |
| [adamic-polblogs] | L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> vp, ep = gt.betweenness(g)
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=vp,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(vp, mi=5, ma=15),
... edge_pen_width=gt.prop_to_size(ep, mi=0.5, ma=5),
... vorder=vp, output="polblogs_betweenness.pdf")
<...>
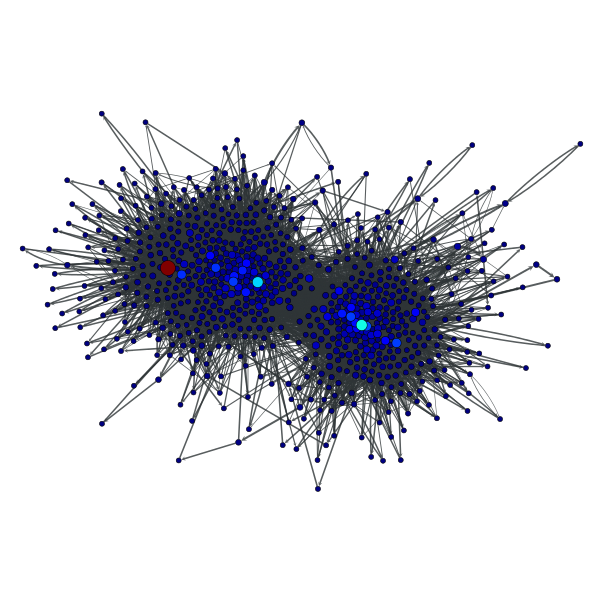
Betweenness values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs].
Calculate the closeness centrality for each vertex.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
weight : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
source : Vertex, optional (default: None)
vprop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
norm : bool, optional (default: True)
harmonic : bool, optional (default: False)
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | vertex_closeness : PropertyMap
|
See also
Notes
The closeness centrality of a vertex \(i\) is defined as,
where \(d_{ij}\) is the (possibly directed and/or weighted) distance from \(i\) to \(j\). In case there is no path between the two vertices, here the distance is taken to be zero.
If harmonic == True, the definition becomes
but now, in case there is no path between the two vertices, we take \(d_{ij} \to\infty\) such that \(1/d_{ij}=0\).
If norm == True, the values of \(c_i\) are normalized by \(n_i-1\) where \(n_i\) is the size of the (out-) component of \(i\). If harmonic == True, they are instead simply normalized by \(N-1\).
The algorithm complexity of \(O(N(N + E))\) for unweighted graphs and \(O(N(N+E) \log N)\) for weighted graphs. If the option source is specified, this drops to \(O(N + E)\) and \(O((N+E)\log N)\) respectively.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
| [closeness-wikipedia] | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Closeness_centrality |
| [opsahl-node-2010] | Opsahl, T., Agneessens, F., Skvoretz, J., “Node centrality in weighted networks: Generalizing degree and shortest paths”. Social Networks 32, 245-251, 2010 DOI: 10.1016/j.socnet.2010.03.006 |
| [adamic-polblogs] | L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> c = gt.closeness(g)
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=c,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(c, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=c, output="polblogs_closeness.pdf")
<...>
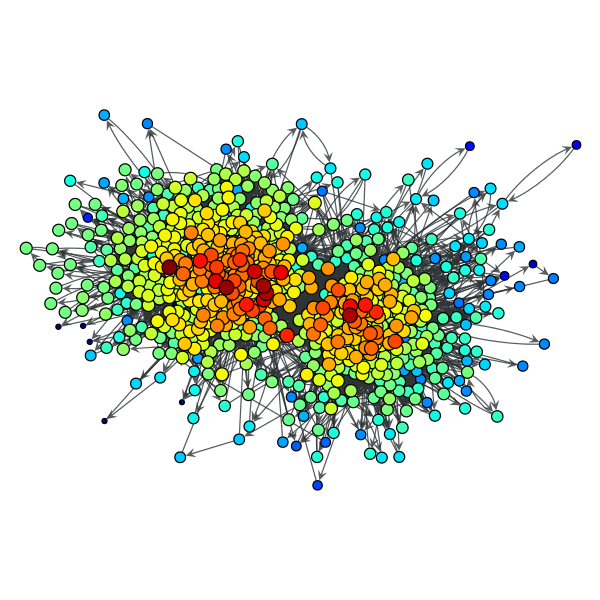
Closeness values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs].
Calculate the central point dominance of the graph, given the betweenness centrality of each vertex.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
betweenness : PropertyMap
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | cp : float
|
See also
Notes
Let \(v^*\) be the vertex with the largest relative betweenness centrality; then, the central point dominance [freeman-set-1977] is defined as:
where \(C_B(v)\) is the normalized betweenness centrality of vertex v. The value of \(C_B\) lies in the range [0,1].
The algorithm has a complexity of \(O(V)\).
References
| [freeman-set-1977] | (1, 2) Linton C. Freeman, “A Set of Measures of Centrality Based on Betweenness”, Sociometry, Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 35-41, 1977, http://www.jstor.org/stable/3033543 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> vp, ep = gt.betweenness(g)
>>> print(gt.central_point_dominance(g, vp))
0.11610685614353008
Calculate the eigenvector centrality of each vertex in the graph, as well as the largest eigenvalue.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
weight : PropertyMap (optional, default: None)
vprop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
epsilon : float, optional (default: 1e-6)
max_iter : int, optional (default: None)
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | eigenvalue : float
eigenvector : PropertyMap
|
See also
Notes
The eigenvector centrality \(\mathbf{x}\) is the eigenvector of the (weighted) adjacency matrix with the largest eigenvalue \(\lambda\), i.e. it is the solution of
where \(\mathbf{A}\) is the (weighted) adjacency matrix and \(\lambda\) is the largest eigenvalue.
The algorithm uses the power method which has a topology-dependent complexity of \(O\left(N\times\frac{-\log\epsilon}{\log|\lambda_1/\lambda_2|}\right)\), where \(N\) is the number of vertices, \(\epsilon\) is the epsilon parameter, and \(\lambda_1\) and \(\lambda_2\) are the largest and second largest eigenvalues of the (weighted) adjacency matrix, respectively.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
| [eigenvector-centrality] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centrality#Eigenvector_centrality |
| [power-method] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_iteration |
| [langville-survey-2005] | A. N. Langville, C. D. Meyer, “A Survey of Eigenvector Methods for Web Information Retrieval”, SIAM Review, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 135-161, 2005, DOI: 10.1137/S0036144503424786 |
| [adamic-polblogs] | L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> w = g.new_edge_property("double")
>>> w.a = np.random.random(len(w.a)) * 42
>>> ee, x = gt.eigenvector(g, w)
>>> print(ee)
0.0013713102236792602
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=x,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(x, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=x, output="polblogs_eigenvector.pdf")
<...>
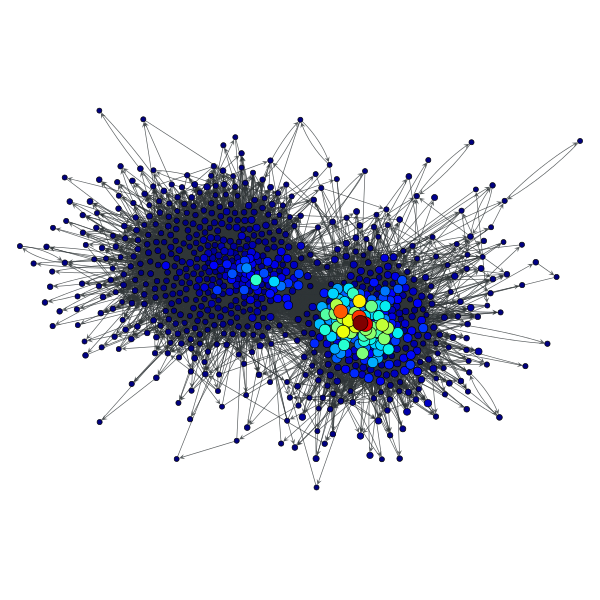
Eigenvector values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs], with random weights attributed to the edges.
Calculate the Katz centrality of each vertex in the graph.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
weight : PropertyMap (optional, default: None)
alpha : float, optional (default: 0.01)
beta : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
vprop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
epsilon : float, optional (default: 1e-6)
max_iter : int, optional (default: None)
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | centrality : PropertyMap
|
See also
Notes
The Katz centrality \(\mathbf{x}\) is the solution of the nonhomogeneous linear system
where \(\mathbf{A}\) is the (weighted) adjacency matrix and \(\mathbf{\beta}\) is the personalization vector (if not supplied, \(\mathbf{\beta} = \mathbf{1}\) is assumed).
The algorithm uses successive iterations of the equation above, which has a topology-dependent convergence complexity.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
| [katz-centrality] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Katz_centrality |
| [katz-new] | L. Katz, “A new status index derived from sociometric analysis”, Psychometrika 18, Number 1, 39-43, 1953, DOI: 10.1007/BF02289026 |
| [adamic-polblogs] | L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> w = g.new_edge_property("double")
>>> w.a = np.random.random(len(w.a)) * 42
>>> x = gt.katz(g, weight=w)
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=x,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(x, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=x, output="polblogs_katz.pdf")
<...>
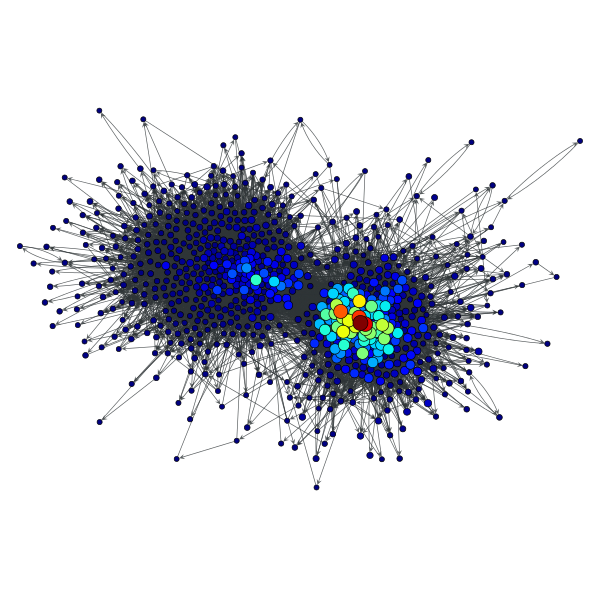
Katz centrality values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs], with random weights attributed to the edges.
Calculate the authority and hub centralities of each vertex in the graph.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
weight : PropertyMap (optional, default: None)
xprop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
yprop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
epsilon : float, optional (default: 1e-6)
max_iter : int, optional (default: None)
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | eig : float
x : PropertyMap
y : PropertyMap
|
See also
Notes
The Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search (HITS) centrality assigns hub (\(\mathbf{y}\)) and authority (\(\mathbf{x}\)) centralities to the vertices, following:
where \(\mathbf{A}\) is the (weighted) adjacency matrix and \(\lambda = 1/(\alpha\beta)\) is the largest eigenvalue of the cocitation matrix, \(\mathbf{A}\mathbf{A}^T\). (Without loss of generality, we set \(\beta=1\) in the algorithm.)
The algorithm uses the power method which has a topology-dependent complexity of \(O\left(N\times\frac{-\log\epsilon}{\log|\lambda_1/\lambda_2|}\right)\), where \(N\) is the number of vertices, \(\epsilon\) is the epsilon parameter, and \(\lambda_1\) and \(\lambda_2\) are the largest and second largest eigenvalues of the (weighted) cocitation matrix, respectively.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
| [hits-algorithm] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HITS_algorithm |
| [kleinberg-authoritative] | J. Kleinberg, “Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked environment”, Journal of the ACM 46 (5): 604-632, 1999, DOI: 10.1145/324133.324140. |
| [power-method] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_iteration |
| [adamic-polblogs] | L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> ee, x, y = gt.hits(g)
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=x,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(x, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=x, output="polblogs_hits_auths.pdf")
<...>
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=y,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(y, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=y, output="polblogs_hits_hubs.pdf")
<...>
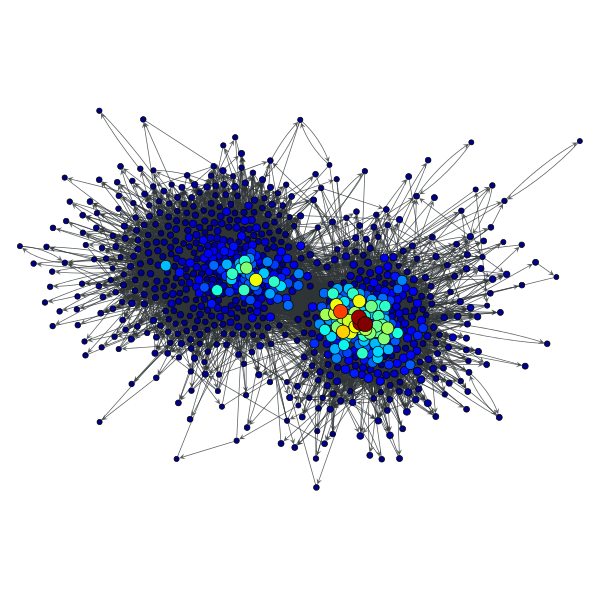
HITS authority values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs].
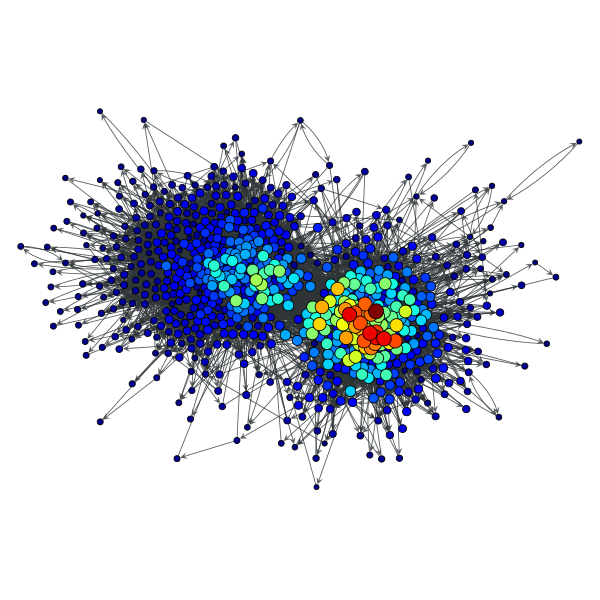
HITS hub values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs].
Calculate the eigentrust centrality of each vertex in the graph.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
trust_map : PropertyMap
vprop : PropertyMap, optional (default: None)
norm : bool, optional (default: False)
epsilon : float, optional (default: 1e-6)
max_iter : int, optional (default: None)
ret_iter : bool, optional (default: False)
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | eigentrust : PropertyMap
|
See also
Notes
The eigentrust [kamvar-eigentrust-2003] values \(t_i\) correspond the following limit
where \(c_i = 1/|V|\) and the elements of the matrix \(C\) are the normalized trust values:
The algorithm has a topology-dependent complexity.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
| [kamvar-eigentrust-2003] | (1, 2) S. D. Kamvar, M. T. Schlosser, H. Garcia-Molina “The eigentrust algorithm for reputation management in p2p networks”, Proceedings of the 12th international conference on World Wide Web, Pages: 640 - 651, 2003, DOI: 10.1145/775152.775242 |
| [adamic-polblogs] | L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> w = g.new_edge_property("double")
>>> w.a = np.random.random(len(w.a)) * 42
>>> t = gt.eigentrust(g, w)
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=t,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(t, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=t, output="polblogs_eigentrust.pdf")
<...>
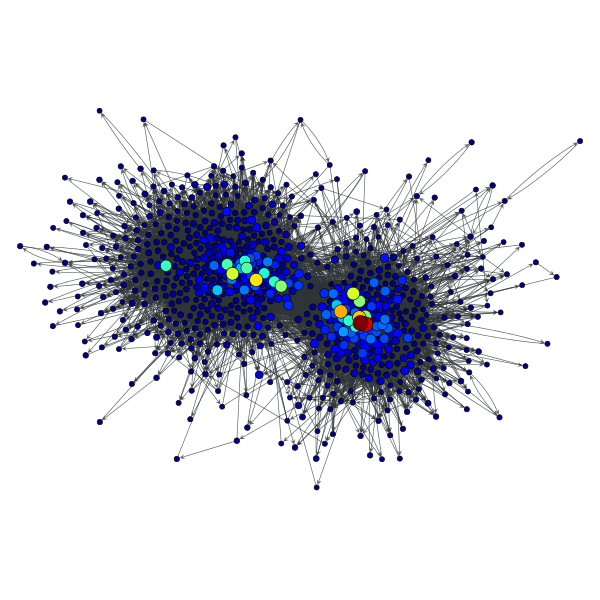
Eigentrust values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs], with random weights attributed to the edges.
Calculate the pervasive trust transitivity between chosen (or all) vertices in the graph.
| Parameters : | g : Graph
trust_map : PropertyMap
source : Vertex (optional, default: None)
target : Vertex (optional, default: None)
vprop : PropertyMap (optional, default: None)
|
|---|---|
| Returns : | trust_transitivity : PropertyMap or float
|
See also
Notes
The pervasive trust transitivity between vertices i and j is defined as
where \(A_{ij}\) is the adjacency matrix, \(c_{ij}\) is the direct trust from i to j, and \(w_G(i\to j)\) is the weight of the path with maximum weight from i to j, computed as
The algorithm measures the transitive trust by finding the paths with maximum weight, using Dijkstra’s algorithm, to all in-neighbours of a given target. This search needs to be performed repeatedly for every target, since it needs to be removed from the graph first. For each given source, the resulting complexity is therefore \(O(N^2\log N)\) for all targets, and \(O(N\log N)\) for a single target. For a given target, the complexity for obtaining the trust from all given sources is \(O(kN\log N)\), where \(k\) is the in-degree of the target. Thus, the complexity for obtaining the complete trust matrix is \(O(EN\log N)\), where \(E\) is the number of edges in the network.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
| [richters-trust-2010] | Oliver Richters and Tiago P. Peixoto, “Trust Transitivity in Social Networks,” PLoS ONE 6, no. 4: e1838 (2011), DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018384 |
| [adamic-polblogs] | L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 |
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"]
>>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g))
>>> g = gt.Graph(g, prune=True)
>>> w = g.new_edge_property("double")
>>> w.a = np.random.random(len(w.a))
>>> g.vp["label"][g.vertex(42)]
'blogforamerica.com'
>>> t = gt.trust_transitivity(g, w, source=g.vertex(42))
>>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=t,
... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(t, mi=5, ma=15),
... vorder=t, output="polblogs_trust_transitivity.pdf")
<...>
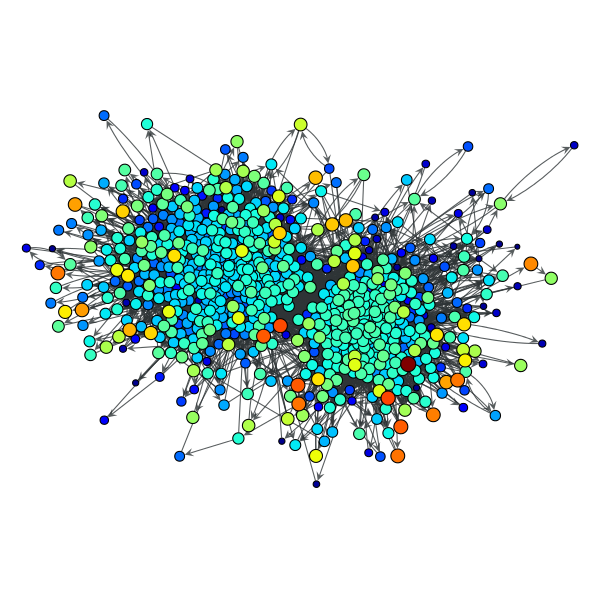
Trust transitivity values from source vertex 42 of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs], with random weights attributed to the edges.